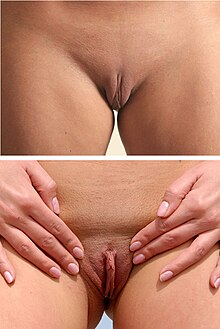
The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora (outer lips) are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the labia minora (inner lips) are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings,[1] as well as the glans clitoris.
In other mammals, the labia majora are not present and the labia minora are instead referred to as the labia vulvae.[2][3][4]
- ^ Blüm, Volker (2012). Vertebrate Reproduction: A Textbook. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 74. ISBN 978-3-64271-074-2. Retrieved November 19, 2023.
- ^ McEntee, Mark (2012). Reproductive Pathology of Domestic Mammals. Elsevier Science. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-32313-804-8. Retrieved November 19, 2023.
- ^ Andrews, Anthony; Boden, Edward (2015). Black's Veterinary Dictionary. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 484. ISBN 978-1-40814-955-3. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- ^ Kumar, M.S.A. (2015). Clinically Oriented Anatomy of the Dog & Cat. Linus Learning. p. 1254. ISBN 978-1-60797-552-6.