| Lactic acid bacteria | |
|---|---|
| |
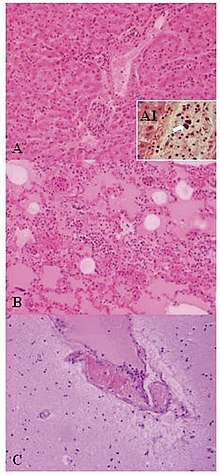
| Lesions of Weissella confusa in the mona monkey (hematoxylin and eosin stain): A) liver: portal triads with neutrophilic infiltration (x10); A1, presence of bacterial emboli inside the vein (arrow) (x40). B) acute pneumonia: edema, congestion, and leukocyte cells exudation in the pulmonary alveoli (x10). C) encephalitis: congestion and marginalized neutrophils in nervous vessels (x10) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Bacillota |
| Class: | Bacilli |
| Order: | Lactobacillales Ludwig, Schleifer & Whitman 2010 |
| Families | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped (bacilli) or spherical (cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB).
Production of lactic acid has linked LAB with food fermentations, as acidification inhibits the growth of spoilage agents. Proteinaceous bacteriocins are produced by several LAB strains and provide an additional hurdle for spoilage and pathogenic microorganisms. Furthermore, lactic acid and other metabolic products contribute to the organoleptic and textural profile of a food item. The industrial importance of the LAB is further evidenced by their generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status, due to their ubiquitous appearance in food and their contribution to the healthy microbiota of animal and human mucosal surfaces.
The genera that comprise the LAB are at its core Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, Lactococcus, and Streptococcus, as well as the more peripheral Aerococcus, Carnobacterium, Enterococcus, Oenococcus, Sporolactobacillus, Tetragenococcus, Vagococcus, and Weissella. All but Sporolactobacillus are members of the Lactobacillales order, and all are members of the Bacillota phylum.
Although lactic acid bacteria are generally associated with the order Lactobacillales, bacteria of the genus Bifidobacterium (phylum Actinomycetota) also produce lactic acid as the major product of carbohydrate metabolism.[1]
- ^ Saez-Lara MJ, Gomez-Llorente C, Plaza-Diaz J, Gil A (2015). "The role of probiotic lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria in the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and other related diseases: a systematic review of randomized human clinical trials". BioMed Research International. 2015: 505878. doi:10.1155/2015/505878. PMC 4352483. PMID 25793197.