| Lake Abitibi | |
|---|---|
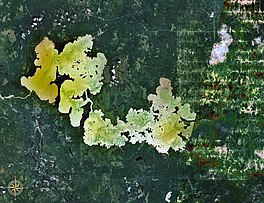 | |
| Location | Cochrane District, Ontario / Abitibi-Ouest Regional County Municipality, Quebec |
| Coordinates | 48°40′N 79°45′W / 48.667°N 79.750°W |
| Primary inflows | Dagenais River, Duparquet River, La Reine River, La Sarre River, Low Bush River |
| Primary outflows | Abitibi River |
| Basin countries | Canada |
| Surface area | 931 km2 (359 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 3.5 m (11 ft) |
| Max. depth | 15.0 m (49.2 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 265 m (869 ft) |
| Islands | over 900 |
Lake Abitibi (French: Lac Abitibi, Ojibwe: Aabitibiiwi-zaaga’igan) is a shallow lake in northeastern Ontario and western Quebec, Canada. The lake, which lies within the vast Clay Belt, is separated in two distinct portions by a short narrows, making it actually two lakes. Its total area is 931 square kilometres (359 sq mi), and net area 903 square kilometres (349 sq mi).[1] The lake is shallow and studded with islands. Its shores and vicinity are covered with small timber.
Its outlet is the Abitibi River, a tributary of the Moose River, which empties into James Bay. The lake takes its name from the river. "Abitibi" comes from the Algonquin words abitah, meaning middle and nipi meaning water,[2] possibly a reference to its geographic location between the Harricana (from the Algonquin word Nanikana, meaning "the main way")[3] to the east and the Kapuskasing–Mattagami river system to the west.
Water levels on the lake are influenced by the Twin Falls Dam on the Abitibi River.
Portions of Lake Abitibi's southern shores and a section of the Abitibi River are part of the Abitibi-de-Troyes Provincial Park. The islands in Ontario's portion of the lake are protected in the Lake Abitibi Islands Provincial Park. The entire McDougall Point Peninsula, that separates the lake in two, is part of the 6,036 hectares (14,920 acres) Mcdougal Point Peninsula Conservation Reserve.[4]
Pointe Abitibi at the mouth of the Duparquet River is a National Historic Site of Canada.[5] This 272 hectares (670 acres) site, known as Apitipik National Historic Site of Canada, was a summer gathering place for the Abitibiwinnik until 1956 and the location of several trading posts between 1686 and 1922.[6]
- ^ Atlas of Canada Archived 2007-04-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Hoiberg, Dale H., ed. (2010). "Abitibi River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. I: A-ak Bayes (15th ed.). Chicago, IL: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc. pp. 33. ISBN 978-1-59339-837-8.
- ^ Environnement Québec, North Harricana River Aquatic Reserve|http://www.mddep.gouv.qc.ca/biodiversite/aquatique/harricana-nord/note-en.pdf Archived 2011-06-16 at the Wayback Machine Online version
- ^ "Crown Land Use Policy Atlas Policy Report C1714: Mcdougal Point Peninsula Conservation Reserve". www.gisapplication.lrc.gov.on.ca. Ministry of Natural Resources. 31 January 2006. Archived from the original on 21 September 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
- ^ "Pointe Abitibi". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ^ "Apitipik National Historic Site of Canada". www.pc.gc.ca. Parks Canada. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 21 September 2021.
