| Large for gestational age | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Macrosomia |
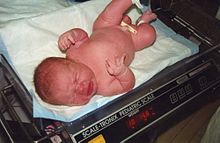 | |
| LGA: A healthy 11-pound (5.0 kg) newborn child, delivered vaginally without complications (41 weeks; fourth child; no gestational diabetes) | |
| Specialty | Obstetrics, pediatrics |
Large for gestational age (LGA) is a term used to describe infants that are born with an abnormally high weight, specifically in the 90th percentile or above, compared to other babies of the same developmental age.[1][2][3] Macrosomia is a similar term that describes excessive birth weight, but refers to an absolute measurement, regardless of gestational age.[4] Typically the threshold for diagnosing macrosomia is a body weight between 4,000 and 4,500 grams (8 lb 13 oz and 9 lb 15 oz), or more, measured at birth, but there are difficulties reaching a universal agreement of this definition.[4]
Evaluating an infant for macrosomia or LGA can help identify risks associated with their birth, including labor complications of both the parent and the child, potential long-term health complications of the child, and infant mortality.[5]
- ^ Szmyd B, Biedrzycka M, Karuga FF, Strzelecka I, Respondek-Liberska M (2021). "Interventricular Septal Thickness as a Diagnostic Marker of Fetal Macrosomia". Journal of Clinical Medicine. 10 (949): 949. doi:10.3390/jcm10050949. PMC 7957748. PMID 33804406.
- ^ Henriksen T (2008). "The macrosomic fetus: a challenge in current obstetrics". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 87 (2): 134–45. doi:10.1080/00016340801899289. PMID 18231880. S2CID 38118355.
- ^ McGrath RT, Glastras SJ, Hocking SL, Fulcher GR (August 2018). "Large-for-Gestational-Age Neonates in Type 1 Diabetes and Pregnancy: Contribution of Factors Beyond Hyperglycemia". Diabetes Care. 41 (8): 1821–1828. doi:10.2337/dc18-0551. PMID 30030258. S2CID 207369659.
- ^ a b Barth Jr WH, Jackson R, et al. (Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics) (January 2020). "Macrosomia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 216". Obstetrics and Gynecology. 135 (1): e18–e35. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000003606. PMID 31856124.
- ^ Boulet SL, Alexander GR, Salihu HM, Pass M (May 2003). "Macrosomic births in the united states: determinants, outcomes, and proposed grades of risk". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 188 (5): 1372–8. doi:10.1067/mob.2003.302. PMID 12748514.