 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Femara, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a698004 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Aromatase inhibitor; Antiestrogen |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 99.9% |
| Protein binding | 60%, mainly to albumin |
| Metabolism | pharmacologically-inactive metabolites Bis(4-cyanophenyl)methanol and 4,4'-dicyanobenzophenone.[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 2 days[3] |
| Excretion | Kidney[3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.200.357 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
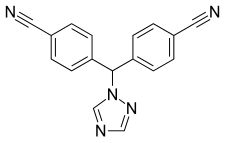
| Formula | C17H11N5 |
| Molar mass | 285.310 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Letrozole, sold under the brand name Femara among others, is an aromatase inhibitor medication that is used in the treatment of breast cancer.[1]
It was patented in 1986 and approved for medical use in 1996.[4] In 2021, it was the 222nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.[5][6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[7]
- ^ a b "Femara- letrozole tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 13 May 2022. Retrieved 28 August 2022.
- ^ "List of nationally authorised medicinal products : Active substance(s): letrozole : Procedure No. PSUSA/00001842/202110" (PDF). Ema.europa.eu. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ a b c "Letrozole". 24 January 2003. Archived from the original on 24 January 2003. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 516. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2021". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ "Letrozole - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 14 January 2024.
- ^ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.