 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Conjupri, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 93% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Excretion | 60% of the metabolites excreted in the urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
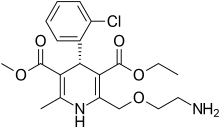
| Formula | C20H25ClN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 408.88 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Levamlodipine (INN), also known as levoamlodipine or S-amlodipine is a pharmacologically active enantiomer of amlodipine.[1] Amlodipine belongs to the dihydropyridine group of calcium channel blocker used as an antihypertensive and antianginal agent.[2] It was approved by the U.S. FDA in December 2019 and is currently marketed under the brand name Conjupri.[3]
- ^ Bhandari P, Shah C, Surwade S (2008-01-01), Chirality-Today and Tomorrow's Way of Treatment, retrieved 2021-10-22
- ^ Thacker HP (April 2007). "S-amlodipine--the 2007 clinical review". Journal of the Indian Medical Association. 105 (4): 180–2, 184, 186 passim. PMID 17822186.
- ^ "Levamlodipine maleate". FDA-Approved Drugs. U.S. Food and Drug Administration.