
Lewy bodies are the inclusion bodies – abnormal aggregations of protein – that develop inside neurons affected by Parkinson's disease (PD), the Lewy body dementias (Parkinson's disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)), and some other disorders.[which?] They are also seen in cases of multiple system atrophy, particularly the parkinsonian variant (MSA-P).[1]
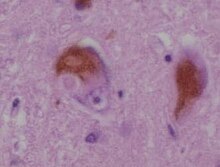
Lewy bodies appear as spherical masses in the cytoplasm that displace other cell components. For instance, some Lewy bodies tend to displace the nucleus to one side of the cell.[2][better source needed] There are two main kinds of Lewy bodies – classical and cortical. A classical Lewy body is an eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion consisting of a dense core surrounded by a halo of 10 nm wide radiating fibrils, the primary structural component of which is alpha-synuclein (α-synuclein). While similar in many other respects, cortical Lewy bodies are only faintly eosinophilic, do not have a surrounding halo, and do not show a radial filamentous substructure.[3] Lewy bodies may be found in the midbrain (within the substantia nigra) or within the cortex.
- ^ Jellinger KA (September 2007). "More frequent Lewy bodies but less frequent Alzheimer-type lesions in multiple system atrophy as compared to age-matched control brains". Acta Neuropathologica. 114 (3): 299–303. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0227-4. PMID 17476513. S2CID 32406286.
- ^ Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (August 1997). "Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies". Nature. 388 (6645): 839–840. Bibcode:1997Natur.388..839G. doi:10.1038/42166. PMID 9278044. S2CID 4419837.
- ^ Mrak, Robert E.; Griffin, W Sue T (October 2007). "Dementia with Lewy bodies: Definition, diagnosis, and pathogenic relationship to Alzheimer's disease". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 3 (5): 619–625. PMC 2656298. PMID 19300591.