This article is about the historical context of Indian languages. For the modern overview, see Languages of India.
Not to be confused with Linguistic Survey of India.
This article contains special characters. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols.
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Linguistic history of India" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
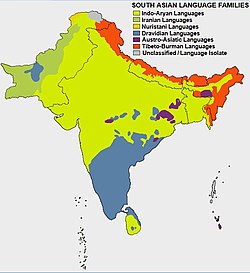
Since the Iron Age in India, the native languages of the Indian subcontinent are divided into various language families, of which the Indo-Aryan and the Dravidian are the most widely spoken. There are also many languages belonging to unrelated language families such as Munda (from Austroasiatic family) and Tibeto-Burman (from Trans-Himalayan family), spoken by smaller groups.
