| |
| |

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
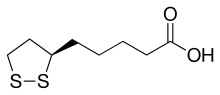
(R)-5-(1,2-Dithiolan-3-yl)pentanoic acid
| |
| Other names
α-Lipoic acid; Alpha lipoic acid; Thioctic acid; 6,8-Dithiooctanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 81851 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.793 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Lipoic+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 206.32 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow needle-like crystals |
| Melting point | 60–62 °C (140–144 °F; 333–335 K) |
| Very Slightly Soluble(0.24 g/L)[1] | |
| Solubility in ethanol 50 mg/mL | Soluble |
| Pharmacology | |
| A16AX01 (WHO) | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| 30% (oral)[2] | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Lipoamide Asparagusic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lipoic acid (LA), also known as α-lipoic acid, alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) and thioctic acid, is an organosulfur compound derived from caprylic acid (octanoic acid).[3] ALA, which is made in animals normally, is essential for aerobic metabolism. It is also available as a dietary supplement or pharmaceutical drug in some countries. Lipoate is the conjugate base of lipoic acid, and the most prevalent form of LA under physiological conditions.[3] Only the (R)-(+)-enantiomer (RLA) exists in nature. RLA is an essential cofactor of many processes.[3]
- ^ "Lipoic Acid". Pubmed. NCBI. Retrieved October 18, 2018.
- ^ Teichert, J; Hermann, R; Ruus, P; Preiss, R (November 2003). "Plasma kinetics, metabolism, and urinary excretion of alpha-lipoic acid following oral administration in healthy volunteers". The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 43 (11): 1257–67. doi:10.1177/0091270003258654. PMID 14551180. S2CID 30589232.
- ^ a b c "Lipoic acid". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis. 1 January 2019. Retrieved 5 November 2019.