This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

The Franks, Germanic-speaking peoples that invaded the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, were first led by individuals called dukes and reguli. The earliest group of Franks that rose to prominence was the Salian Merovingians, who conquered most of Roman Gaul, as well as the Gaulish territory of the Visigothic Kingdom, following the Battle of Vouillé in 507 AD.
The sons of Clovis I, the first King of the Franks, conquered the Burgundian and the Alamanni Kingdoms. They acquired Provence, and went on to make the peoples of the Bavarii and Thuringii their clients. The Merovingians were later replaced by the new Carolingian dynasty in the 8th century. By the late 10th century, the Carolingians themselves had been replaced throughout much of their realm by other dynasties.
A timeline of Frankish rulers has been difficult to trace since the realm, according to old Germanic practice, was frequently divided among the sons of a king upon the king's death. However, territories were eventually reunited through marriage, treaty or conquest. There were often multiple Frankish kings who ruled different territories, and divisions of the territories were not very consistent over time.
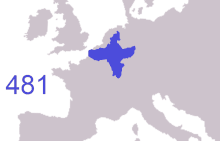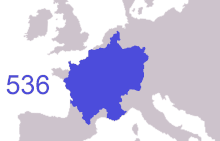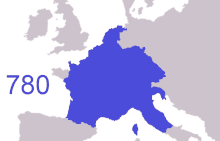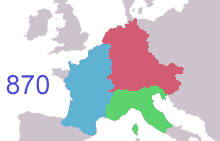
As inheritance traditions changed over time, the divisions of Francia (the lands of the Franks) started to become kingdoms that were more permanent. West Francia formed the heart of what was to become the Kingdom of France; East Francia evolved into the Kingdom of Germany; and Middle Francia became the Kingdom of Lotharingia in the north, the Kingdom of Italy in the south, and the Kingdom of Provence in the west. West and East Francia soon divided up the area of Middle Francia.
The idea of a "King of the Franks" (Rex Francorum) gradually disappeared. The title "King of the Franks" is attested in the Kingdom of France until 1190, that of "Queen of the Franks" (for queen consorts) until 1227. That represented a shift in thinking about the monarchy from that of a popular monarchy, the leader of a people, sometimes without a defined territory to rule, to that of a monarchy tied to a specific territory.