It has been suggested that this article should be split into articles titled lithium titanate, lithium titanate spinel and lithium metatitanate. (discuss) (May 2022) |

| |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lithium metatitanate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.586 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li2TiO3 | |
| Molar mass | 109.76 |
| Appearance | White powder[1] |
| Density | 3.43 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 1,533 °C (2,791 °F; 1,806 K)[1] |
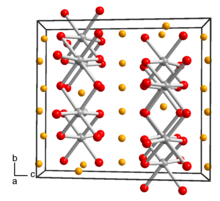
| Structure[3] | |
| Monoclinic, mS48, No. 15 | |
| C2/c | |
a = 0.505 nm, b = 0.876 nm, c = 0.968 nm α = 90°°, β = 100°°, γ = 90°°
| |
Lattice volume (V)
|
0.4217 nm3 |
Formula units (Z)
|
8 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lithium titanates are chemical compounds of lithium, titanium and oxygen. They are mixed oxides and belong to the titanates. The most important lithium titanates are:
- lithium titanate spinel, Li4Ti5O12 and the related compounds up to Li7Ti5O12. These titanates are used in lithium-titanate batteries.
- lithium metatitanate, a compound with the chemical formula Li2TiO3 and a melting point of 1,533 °C (2,791 °F)[4] It is a white powder with possible applications in tritium breeding materials in nuclear fusion applications.
Other lithium titanates, i.e. mixed oxides of the system Li2O–TiO2, are:
- Lithium orthotitanate Li4TiO4, melting point of 1,200 °C (2,190 °F)[4]
- Ramsdellite lithium titanate Li2Ti3O7 and LixTiO2 (0 ≦ x ≦ 0.57) with ramsdellite structure.[5]
- ^ a b Hanaor, Dorian A.H.; Kolb, Matthias H.H.; Gan, Yixiang; Kamlah, Marc; Knitter, Regina (2014). "Solution based synthesis of mixed-phase materials in the Li2TiO3-Li4SiO4 system". Journal of Nuclear Materials. 456: 151–161. arXiv:1410.7128. Bibcode:2015JNuM..456..151H. doi:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2014.09.028. S2CID 94426898.
- ^ Van Der Laan, J.G; Muis, R.P (1999). "Properties of lithium metatitanate pebbles produced by a wet process". Journal of Nuclear Materials. 271–272: 401–404. Bibcode:1999JNuM..271..401V. doi:10.1016/S0022-3115(98)00794-6.
- ^ Claverie J., Foussier C., Hagenmuller P. (1966) Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 244-246
- ^ a b Dorian Hanaor; Matthias Kolb; Yixiang Gan; Marc Kamlah; Regina Knitter (2014). "Mixed phase materials in the Li4SiO4 Li2TiO3 system". Journal of Nucl Materials. 456: 151–166.
- ^ Tsuyumoto, Isao; Moriguchi, Takumi (October 2015). "Synthesis and lithium insertion properties of ramsdellite LixTiO2 anode materials". Materials Research Bulletin. 70: 748–752. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2015.06.014.