| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
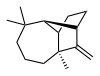
| IUPAC name
(1R,2S,7S,9S)- 3,3,7-trimethyl- 8-methylenetricyclo- [5.4.0.02,9]undecane
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 5731712 2044263 4663756 | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.812 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.36 g/mol |
| Density | 0.928 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 254 °C (489 °F; 527 K) (706 mm Hg) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H304, H317, H410 | |
| P261, P272, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P321, P331, P333+P313, P363, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Longifolene is the common (or trivial) chemical name of a naturally occurring, oily liquid hydrocarbon found primarily in the high-boiling fraction of certain pine resins. The name is derived from that of a pine species from which the compound was isolated,[1] Chemically, longifolene is a tricyclic sesquiterpene. This molecule is chiral, and the enantiomer commonly found in pines and other higher plants exhibits a positive optical rotation of +42.73°. The other enantiomer (optical rotation −42.73°) is found in small amounts in certain fungi and liverworts.
Longifolene is also one of two most abundant aroma constituents of lapsang souchong tea, because the tea is smoked over pinewood fires.[2]
- ^ Naffa, P.; Ourisson, G. Bulletin de la Société chimique de France, 1954, 1410.
- ^ Shan-Shan Yao; Wen-Fei Guo; YI Lu; Yuan-Xun Jiang, "Flavor Characteristics of Lapsang Souchong and Smoked Lapsang Souchong,a Special Chinese Black Tea with Pine Smoking Process", Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, Vol. 53, No.22, (2005)[permanent dead link]