 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xefo, Xefocam others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, parenteral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90–100% |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | CYP2C9 |
| Elimination half-life | 3–4 hours |
| Excretion | 2/3 liver, 1/3 kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.158.646 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
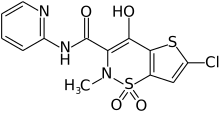
| Formula | C13H10ClN3O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 371.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lornoxicam, also known as chlortenoxicam, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the oxicam class with analgesic (pain relieving), anti-inflammatory and antipyretic (fever reducing) properties. It is available in oral and parenteral formulations.
It was patented in 1977 and approved for medical use in 1997.[1] Brand names include Xefo and Xefocam among others.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 519. ISBN 9783527607495.