 An illustration of the Gateway's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) and Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) in orbit around the Moon | |
 | |
| Station statistics | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 4 maximum (planned) |
| Launch | 2027 (planned)[1] |
| Carrier rocket | Falcon Heavy SLS Block 1B |
| Launch pad | Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 |
| Mission status | In development |
| Pressurised volume | ≥125 m3 (4,400 cu ft) (planned)[2] |
| Periselene altitude | 3,000 km (1,900 mi)[3] |
| Aposelene altitude | 70,000 km (43,000 mi) |
| Orbital inclination | Polar near-rectilinear halo orbit (NRHO) |
| Orbital period | ≈7 days |
| Configuration | |
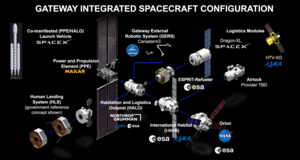 Configuration as of 16 November 2022 | |
| Part of a series on the |
| United States space program |
|---|
  |
The Lunar Gateway, or simply Gateway, is a space station which is planned to be assembled in orbit around the Moon. The Gateway is intended to serve as a communication hub, science laboratory, and habitation module for astronauts as part of the Artemis program. It is a multinational collaborative project: participants include NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), and the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC). The Gateway is planned to be the first space station beyond low Earth orbit.[4][5]
The science disciplines to be studied on the Gateway are expected to include planetary science, astrophysics, Earth observation, heliophysics, fundamental space biology, and human health and performance.[6] As of April 2024, construction is underway of the initial habitation and propulsion modules.[7][8][9] The International Space Exploration Coordination Group (ISECG), which is composed of 14 space agencies including NASA, has concluded that Gateway systems will be critical in expanding human presence to the Moon, to Mars, and deeper into the Solar System.[10]
The project is expected to play a major role in the Artemis program after 2024. NASA's Budget for FY 2025 included $817.7 million for the project.[11] While the project is led by NASA, the Gateway is meant to be developed, serviced, and used in collaboration with the CSA, ESA, JAXA, and commercial partners. It will serve as the staging point for both robotic and crewed exploration of the lunar south pole and is the proposed staging point for NASA's Deep Space Transport concept for transport to Mars.[12][7][13]
- ^ "Artemis Programs: NASA Should Document and Communicate Plans to Address Gateway's Mass Risk". GAO. 31 July 2024. Retrieved 31 July 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
nsf-20180911was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
NRHO 2019was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "FY 2022: NASA Budget Request" (PDF). NASA. 28 May 2021. Retrieved 1 June 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Jackson, Shanessa (11 September 2018). "Competition Seeks University Concepts for Gateway and Deep Space Exploration Capabilities". nasa.gov. NASA. Archived from the original on 17 June 2019. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Mahoney, Erin (24 August 2018). "NASA Seeks Ideas for Scientific Activities Near the Moon". nasa.gov. NASA. Archived from the original on 9 June 2019. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b Hambleton, Kathryn (28 March 2017). "Deep Space Gateway to Open OpportunitiesArtemis for Distant Destinations". nasa.gov. NASA. Archived from the original on 27 September 2017. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "РОСКОСМОС – NASA СОВМЕСТНЫЕ ИССЛЕДОВАНИЯ ДАЛЬНЕГО КОСМОСА (ROSCOSMOS – NASA JOINT RESEARCH OF FAR COSMOS)" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 10 September 2019. Retrieved 29 September 2017.
- ^ Weitering, Hanneke (27 September 2017). "NASA and Russia Partner Up for Crewed Deep-Space Missions". Space.com. Archived from the original on 10 September 2019. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
- ^ NASA (2 May 2018). "Gateway Memorandum for the Record" (PDF). nasa.gov. NASA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 July 2019. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "FY 2025 Budget Estimates" (PDF).
- ^ Gebhardt, Chris (6 April 2017). "NASA finally sets goals, missions for SLS – eyes multi-step plan to Mars". nasaspaceflight.com. NASASpaceflight. Archived from the original on 21 August 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2018.
- ^ Gatens, Robyn; Crusan, Jason. "Cislunar Habitation and Environmental Control and Life Support System" (PDF). nasa.gov. NASA. Retrieved 31 March 2017.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.