| Madeira River | |
|---|---|
 The river in the outskirts of Porto Velho | |
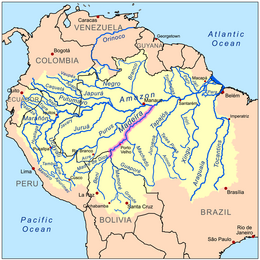
 Map of the Madeira River watershed | |
| Etymology | Portuguese, "wood river" |
| Location | |
| Country | Bolivia, Brazil |
| Cities | Nova Olinda do Norte, Borba, Novo Aripuanã, Manicoré, Humaitá, Porto Velho |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Confluence of Madre de Dios and Mamoré[1][2] |
| • location | Near Guayaramerín, Bolivia |
| • coordinates | 10°38′19″S 65°39′20″W / 10.63861°S 65.65556°W |
| • elevation | 180 m (590 ft) |
| Mouth | Amazon River |
• location | Amazonas, Brazil |
• coordinates | 3°22′32″S 58°46′23″W / 3.37556°S 58.77306°W |
• elevation | 40 m (130 ft) |
| Length | 1,450 km (900 mi)[3] |
| Basin size | 1,376,000 km2 (531,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | near mouth |
| • average | (Period: 1973–1990)31,200 m3/s (1,100,000 cu ft/s) |
| • minimum | 2,346 m3/s (82,800 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 52,804 m3/s (1,864,800 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Amazon → Atlantic Ocean |
| River system | Amazon |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Madre de Dios, Abunã |
| • right | Mamoré, Jamari, Ji-Paraná, Marmelos, Manicoré, Mataurá, Mariepauá, Aripuanã |
The Madeira River (Portuguese: Rio Madeira [maˈdejɾɐ]) is a major waterway in South America. It is estimated to be 1,450 km (900 mi) in length, while the Madeira-Mamoré is estimated near 3,250 km (2,020 mi)[4] or 3,380 km (2,100 mi) in length depending on the measuring party and their methods. The Madeira is the biggest tributary of the Amazon, accounting for about 15% of the water in the basin.[5] A map from Emanuel Bowen in 1747, held by the David Rumsey Map Collection, refers to the Madeira by the pre-colonial, indigenous name Cuyari.[6]
The River of Cuyari, called by the Portuguese Madeira or the Wood River, is formed by two great rivers, which join near its mouth. It was by this River, that the Nation of Topinambes passed into the River Amazon.
- ^ R. Ziesler and G.D. Ardizzone. LAS AGUAS CONTINENTALES DE AMERICA LATINA/THE INLAND WATERS OF LATIN AMERICA, Fishery Information, Data and Statistics Service. Fisheries Department FAO, Rome.
- ^ Madeira, Visuotinė lietuvių enciklopedija
- ^ Ziesler, R.; Ardizzone, G.D. (1979). "Amazon River System". The Inland waters of Latin America. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 92-5-000780-9. Archived from the original on 21 October 2013.
- ^ "Madeira (river)". Talktalk.co.uk (encyclopedia). Accessed May 2011.
- ^ "Waters". Amazon Waters. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ^ "Peru, Amazones. - David Rumsey Historical Map Collection". www.davidrumsey.com. Retrieved 16 April 2018.