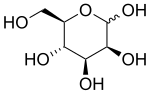
 D-Mannopyranose
| |
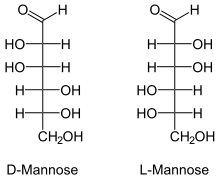 Fischer projections
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Mannose
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3S,4S,5S,6R)-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol | |
| Identifiers | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Mannose |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 180.156 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.554 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 132 °C (270 °F; 405 K) |
| -102.90·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mannose is a sugar with the formula HOCH2(CHOH)4CHO. It is one of the monomers of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. It is a C-2 epimer of glucose. Mannose is important in human metabolism, especially in the glycosylation of certain proteins. Several congenital disorders of glycosylation are associated with mutations in enzymes involved in mannose metabolism.[1]
Mannose is not an essential nutrient; it can be produced in the human body from glucose, or converted into glucose. Mannose provides 2–5 kcal/g. It is partially excreted in the urine.
- ^ Freeze, H. H.; Sharma, V. (2010). "Metabolic manipulation of glycosylation disorders in humans and animal models". Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 21 (6): 655–662. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.03.011. PMC 2917643. PMID 20363348.