This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (November 2021) |
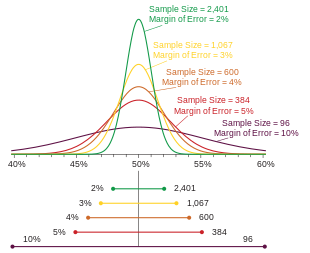
The margin of error is a statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in the results of a survey. The larger the margin of error, the less confidence one should have that a poll result would reflect the result of a census of the entire population. The margin of error will be positive whenever a population is incompletely sampled and the outcome measure has positive variance, which is to say, whenever the measure varies.
The term margin of error is often used in non-survey contexts to indicate observational error in reporting measured quantities.