 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Inversine, Vecamyl |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 40% |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.433 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
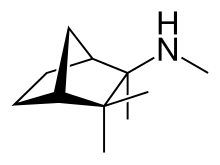
| Formula | C11H21N |
| Molar mass | 167.296 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Mecamylamine (INN, BAN; or mecamylamine hydrochloride (USAN); brand names Inversine, Vecamyl[1]) is a non-selective, non-competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) that was introduced in the 1950s as an antihypertensive drug.[2] In the United States, it was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in 2009 but was brought to market in 2013 as Vecamyl and eventually was marketed by Turing Pharmaceuticals.[3][4]
Chemically, mecamylamine is a secondary aliphatic amine, with a pKaH of 11.2[5]
- ^ "Mecamylamine". drugs.com. Retrieved May 15, 2015.
- ^ Bacher I, Wu B, Shytle DR, George TP (November 2009). "Mecamylamine - a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist with potential for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 10 (16): 2709–2721. doi:10.1517/14656560903329102. PMID 19874251. S2CID 25690407.
- ^ "Drug Profile: Mecamylamine - Targacept". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- ^ "Drugs@FDA: FDA Approved Drug Products". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 2017-10-16.
- ^ Schanker LS, Shore PA, Brodie BB, Hogben CA (August 1957). "Absorption of drugs from the stomach. I. The rat". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 120 (4): 528–539. PMID 13476377.