| Medial lemniscus | |
|---|---|
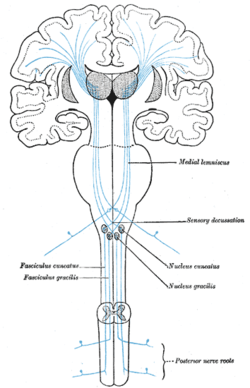 The sensory tract. (Medial lemniscus labeled at top right.) | |
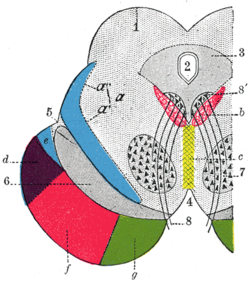 Coronal section through mid-brain. ("e" is Portion of medial lemniscus, which runs to the lentiform nucleus and insula. "a’" is also the medial lemniscus.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lemniscus medialis |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_887 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.111 A14.1.08.672 A14.1.06.207 |
| TA2 | 5861 |
| FMA | 83675 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The medial lemniscus, also known as Reil's band or Reil's ribbon (for German anatomist Johann Christian Reil), is a large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons that decussate in the brainstem, specifically in the medulla oblongata. The medial lemniscus is formed by the crossings of the internal arcuate fibers. The internal arcuate fibers are composed of axons of the gracile nucleus and the cuneate nucleus. The cell bodies of the nuclei lie contralaterally.
The medial lemniscus is part of the somatosensory dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway, which ascends in the spinal cord to the thalamus.[1] Lesions of the medial lemniscus cause an impairment of vibratory and touch-pressure sense.
- ^ Kamali A, Kramer LA, Butler IJ, Hasan KM. Diffusion tensor tractography of the somatosensory system in the human brainstem: initial findings using high isotropic spatial resolution at 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2009 19:1480-8. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1305-x.