| Mekong River 湄公河 (Méigōng Hé) / 澜沧江 (Láncāng Jiāng) မဲခေါင်မြစ် (Megaung Myit) ແມ່ນ້ຳຂອງ (Maenam Khong) แม่น้ำโขง (Maenam Khong) ទន្លេមេគង្គ (Tônlé Mékôngk) Sông Mê Kông / Sông Cửu Long (九龍) | |
|---|---|
 Mekong River, Luang Prabang, Laos | |
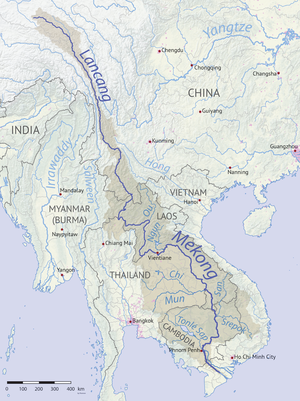 Mekong River watershed | |
| Location | |
| Country | China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Lasaigongma (拉赛贡玛) Spring |
| • location | Mt. Guozongmucha (果宗木查), Zadoi, Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Qinghai, |
| • coordinates | 33°42.5′N 94°41.7′E / 33.7083°N 94.6950°E |
| • elevation | 5,224 m (17,139 ft) |
| Mouth | Mekong Delta |
• location | Vietnam |
• coordinates | 10°11′N 106°45′E / 10.19°N 106.75°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 4,350 km (2,700 mi) |
| Basin size | 795,000 km2 (307,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Mekong Delta, South China Sea |
| • average | 16,000 m3/s (570,000 cu ft/s) |
| • minimum | 1,400 m3/s (49,000 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 39,000 m3/s (1,400,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Srepok, Nam Khan, Tha, Nam Ou |
| • right | Mun, Tonlé Sap, Kok, Ruak |
 | |
The Mekong or Mekong River is a trans-boundary river in East Asia and Southeast Asia. It is the world's twelfth-longest river and the third-longest in Asia[1] with an estimated length of 4,909 km (3,050 mi)[1] and a drainage area of 795,000 km2 (307,000 sq mi), discharging 475 km3 (114 cu mi) of water annually.[2] From its headwaters in the Tibetan Plateau, the river runs through Southwest China (where it is officially called the Lancang River), Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, and southern Vietnam. The extreme seasonal variations in flow and the presence of rapids and waterfalls in the Mekong make navigation difficult. Even so, the river is a major trade route between Tibet and Southeast Asia. The construction of hydroelectric dams along the Mekong in the 2000s through the 2020s has caused serious problems for the river's ecosystem, including the exacerbation of drought.[3][4][5]
- ^ a b S. Liu; P. Lu; D. Liu; P. Jin; W. Wang (2009). "Pinpointing source and measuring the lengths of the principal rivers of the world". International Journal of Digital Earth. 2 (1): 80–87. Bibcode:2009IJDE....2...80L. doi:10.1080/17538940902746082. S2CID 27548511.
- ^ "State of the Basin Report, 2010" (PDF). Mekong River Commission. Vientiane. 2010.
- ^ Sasipornkarn, Emmy (16 August 2019). "A dam-building race threatens the Mekong River". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 18 August 2019.
- ^ Sripiachai, Pattanapong (29 October 2019). "Mekong River falls to critical level, sand dunes emerge". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 26 November 2019.
- ^ Beech, Hannah (13 April 2020). "China Limited the Mekong's Flow. Other Countries Suffered a Drought". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 14 April 2020.