| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
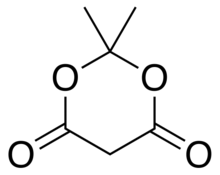
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione | |
| Other names
Isopropylidene malonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.358 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 144.126 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 94 to 95 °C (201 to 203 °F; 367 to 368 K) (decomposes)[1] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.97 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Meldrum's acid or 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione is an organic compound with formula C6H8O4. Its molecule has a heterocyclic core with four carbon and two oxygen atoms; the formula can also be written as [−O−(C(CH3)2)−O−(C=O)−(CH2)−(C=O)−].
It is a crystalline colorless solid, sparingly soluble in water. It decomposes on heating with release of carbon dioxide and acetone.[2][3]
- ^ "Meldrum's Acid". The Merck Index. 14th. Vol. edition. Merck Research Laboratories. 2006. p. 1005. ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1.
- ^ McNab, Hamish (1978). "Meldrum's acid". Chemical Society Reviews. 7 (3): 345–358. doi:10.1039/CS9780700345.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
meldrumwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).