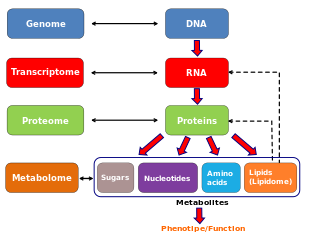
The metabolome refers to the complete set of small-molecule chemicals found within a biological sample.[1] The biological sample can be a cell, a cellular organelle, an organ, a tissue, a tissue extract, a biofluid or an entire organism. The small molecule chemicals found in a given metabolome may include both endogenous metabolites that are naturally produced by an organism (such as amino acids, organic acids, nucleic acids, fatty acids, amines, sugars, vitamins, co-factors, pigments, antibiotics, etc.) as well as exogenous chemicals (such as drugs, environmental contaminants, food additives, toxins and other xenobiotics) that are not naturally produced by an organism.[2][3]
In other words, there is both an endogenous metabolome and an exogenous metabolome. The endogenous metabolome can be further subdivided to include a "primary" and a "secondary" metabolome (particularly when referring to plant or microbial metabolomes). A primary metabolite is directly involved in the normal growth, development, and reproduction. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has important ecological function. Secondary metabolites may include pigments, antibiotics or waste products derived from partially metabolized xenobiotics. The study of the metabolome is called metabolomics.
- ^ Oliver SG, Winson MK, Kell DB, Baganz F (September 1998). "Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome". Trends in Biotechnology. 16 (9): 373–8. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.33.5221. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(98)01214-1. PMID 9744112.
- ^ Wishart DS (September 2007). "Current progress in computational metabolomics". Briefings in Bioinformatics. 8 (5): 279–93. doi:10.1093/bib/bbm030. PMID 17626065.
- ^ Nordström A, O'Maille G, Qin C, Siuzdak G (May 2006). "Nonlinear data alignment for UPLC-MS and HPLC-MS based metabolomics: quantitative analysis of endogenous and exogenous metabolites in human serum". Analytical Chemistry. 78 (10): 3289–95. doi:10.1021/ac060245f. PMC 3705959. PMID 16689529.