| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methanediol[1] | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | MADOL | ||
| 1730798 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.673 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH4O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 48.041 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 1.199 g/cm3 [citation needed] | ||
| Boiling point | 194 °C (381 °F; 467 K) at 101 kPa [citation needed] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 16.1 Pa [citation needed] | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.29[2] | ||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.401 [citation needed] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Flash point | 99.753 °C (211.555 °F; 372.903 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
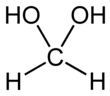
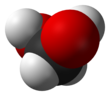
Methanediol, also known as formaldehyde monohydrate or methylene glycol, is an organic compound with chemical formula CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest geminal diol. In aqueous solutions it coexists with oligomers (short polymers). The compound is closely related and convertible to the industrially significant derivatives paraformaldehyde ((CH2O)n), formaldehyde (H2C=O), and 1,3,5-trioxane ((CH2O)3).[3]
Methanediol is a product of the hydration of formaldehyde. The equilibrium constant for hydration is estimated to be 103,[4]CH2(OH)2 predominates in dilute (<0.1%) solution. In more concentrated solutions, it oligomerizes to HO(CH2O)nH.[3]
- ^ "Methanediol - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 20 October 2011.
- ^ Bell, R. P.; McTigue, P. T. (1960). "603. Kinetics of the aldol condensation of acetaldehyde". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2983. doi:10.1039/JR9600002983.
- ^ a b Reuss, Günther; Disteldorf, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Hilt, Albrecht (2000). "Formaldehyde". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_619. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ Eric V. Anslyn, Dennis A. Dougherty (2006), Modern physical organic chemistry. University Science Books. ISBN 1-891389-31-9. 1095 pages