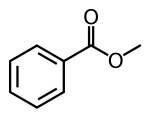
| |||

| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl benzoate | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methyl benzenecarboxylate | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.055 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.0837 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −12.5 °C (9.5 °F; 260.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 199.6 °C (391.3 °F; 472.8 K) | ||
| −81.95×10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5164 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 82 °C (180 °F; 355 K) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ScienceLab MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Methyl benzoate is an organic compound. It is an ester with the chemical formula C6H5COOCH3, sometimes abbreviated as PhCO2Me, where Ph and Me are phenyl and methyl, respectively. Its structure is C6H5−C(=O)−O−CH3. It is a colorless liquid that is poorly soluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Methyl benzoate has a pleasant smell, strongly reminiscent of the fruit of the feijoa tree, and it is used in perfumery. It also finds use as a solvent and as a pesticide used to attract insects such as orchid bees.