 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oblivon |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.960 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
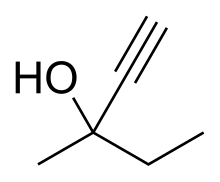
| Formula | C6H10O |
| Molar mass | 98.145 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Methylpentynol (Methylparafynol, Dormison, Atemorin, Oblivon) is a tertiary pentynol with hypnotic/sedative and anticonvulsant effects and an exceptionally low therapeutic index. It was discovered by Bayer in 1913[2] and was used shortly thereafter for the treatment of insomnia, but its use was quickly phased out in response to newer drugs with far more favorable safety profiles.[3][4][5]
The drug was marketed again in the United States, Europe and elsewhere from 1956 well into the 1960s as a rapid-acting sedative.[6] The drug was quickly overshadowed at that point by benzodiazepines and is no longer sold anywhere.[7]
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ DE patent 289800, "Verfahren zur Darstellung der Oxyalkylderivate von Kohlenwasserstoffen", issued 1913-11-30, assigned to Bayer, Leverkusen
- ^ Hirsh HL, Orsinger WH (January 1952). "Methylparafynol--a new type hypnotic. Preliminary report on its therapeutic efficacy and toxicity". American Practitioner and Digest of Treatment. 3 (1): 23–6. PMID 14903452.
- ^ Schaffarzick RW, Brown BJ (December 1952). "The anticonvulsant activity and toxicity of methylparafynol (dormison) and some other alcohols". Science. 116 (3024): 663–5. Bibcode:1952Sci...116..663S. doi:10.1126/science.116.3024.663. PMID 13028241.
- ^ Herz A (March 1954). "[A new type of hypnotic; unsaturated tertiary carbinols; experimental studies on therapeutic use of 3-methyl-pentin-ol-3 (methylparafynol)]". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 4 (3): 198–9. PMID 13159700.
- ^ Weaver LC, Alexander WM, Abreu BE (April 1961). "Anticonvulsant activity of compounds related to methylparafynol". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. 131: 116–22. PMID 13783544.
- ^ Hines RD (2002). The Pursuit of Oblivion. p. 327.