| Ministeria vibrans | |
|---|---|
| |
| Ministeria vibrans | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Patterson, Nygaard, Steinberg & Turley, 1993[1]
|
| Species: | M. vibrans
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ministeria vibrans Tong, 1997
| |
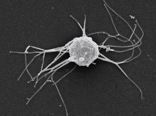
Ministeria vibrans is a bacterivorous amoeba with filopodia that was originally described to be suspended by a flagellum-like stalk attached to the substrate. Molecular and experimental work later on demonstrated the stalk is indeed a flagellar apparatus.[2]
The amoeboid protist Ministeria vibrans occupies a key position in understanding animal origins. It is a member of the Filasterea, that is the sister-group to Choanoflagellatea and Metazoa.[2][3] Two Ministeria amoebae species have been reported so far,[4] both of them from coastal marine water samples: M. vibrans and M. marisola.[1] However, there is currently only one culture available, that of Ministeria vibrans.
The life cycle of Ministeria remains unknown.
Microvilli in Ministeria suggest their presence in the common ancestor of Filasterea and Choanoflagellata. The kinetid structure of Ministeria is similar to that of the choanocytes of the most deep-branching sponges, differing essentially from the kinetid of choanoflagellates. Thus, kinetid and microvilli of Ministeria illustrate features of the common ancestor of three holozoan groups: Filasterea, Metazoa and Choanoflagellata.[5]
- ^ a b Patterson, David J.; Nygaard, Kari; Steinberg, Gero; Turley, Carol M. (11 May 2009). "Heterotrophic flagellates and other protists associated with oceanic detritus throughout the water column in the mid North Atlantic". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 73 (1): 67–95. doi:10.1017/S0025315400032653.
- ^ a b Torruella, Guifré; Derelle, Romain; Paps, Jordi; Lang, B. Franz; Roger, Andrew J.; Shalchian-Tabrizi, Kamran; Ruiz-Trillo, Iñaki (2012). "Phylogenetic Relationships within the Opisthokonta Based on Phylogenomic Analyses of Conserved Single-Copy Protein Domains". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 29 (2): 531–544. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr185. PMC 3350318. PMID 21771718.
- ^ Torruella, Guifré; de Mendoza, Alex; Grau-Bové, Xavier; Antó, Meritxell; Chaplin, Mark A.; del Campo, Javier; Eme, Laura; Pérez-Cordón, Gregorio; Whipps, Christopher M.; Nichols, Krista M.; Paley, Richard; Roger, Andrew J.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, Ariadna; Donachie, Stuart; Ruiz-Trillo, Iñaki (September 2015). "Phylogenomics Reveals Convergent Evolution of Lifestyles in Close Relatives of Animals and Fungi". Current Biology. 25 (18): 2404–2410. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.07.053. PMID 26365255.
- ^ Tong, Susan M. (November 1997). "Heterotrophic flagellates and other protists from Southampton Water, U.K.". Ophelia. 47 (2): 71–131. doi:10.1080/00785236.1997.10427291.
- ^ Mylnikov, Alexander P.; Tikhonenkov, Denis V.; Karpov, Sergey A.; Wylezich, Claudia (1 August 2019). "Microscopical Studies on Ministeria vibrans Tong, 1997 (Filasterea) Highlight the Cytoskeletal Structure of the Common Ancestor of Filasterea, Metazoa and Choanoflagellata". Protist. 170 (4): 385–396. doi:10.1016/j.protis.2019.07.001. PMID 31493690.