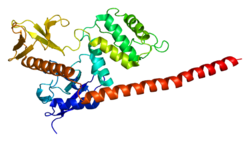
Moesin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSN gene.[5][6]
Moesin (for membrane-organizing extension spike protein) is a member of the ERM protein family which includes ezrin and radixin. ERM proteins appear to function as cross-linkers between plasma membranes and actin-based cytoskeletons.[7]
Moesin is localized to filopodia and other membranous protrusions that are important for cell–cell recognition and signaling and for cell movement.[7]
Moesin has FERM domain at N-terminal.
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000147065 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031207 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Lankes WT, Furthmayr H (Oct 1991). "Moesin: a member of the protein 4.1-talin-ezrin family of proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (19): 8297–301. Bibcode:1991PNAS...88.8297L. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.19.8297. PMC 52495. PMID 1924289.
- ^ Amieva MR, Furthmayr H (Sep 1995). "Subcellular localization of moesin in dynamic filopodia, retraction fibers, and other structures involved in substrate exploration, attachment, and cell-cell contacts". Exp. Cell Res. 219 (1): 180–96. doi:10.1006/excr.1995.1218. PMID 7628534.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: MSN moesin".