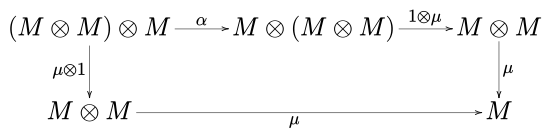In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a monoid (or monoid object, or internal monoid, or algebra) (M, μ, η) in a monoidal category (C, ⊗, I) is an object M together with two morphisms
- μ: M ⊗ M → M called multiplication,
- η: I → M called unit,
such that the pentagon diagram
and the unitor diagram
commute. In the above notation, 1 is the identity morphism of M, I is the unit element and α, λ and ρ are respectively the associativity, the left identity and the right identity of the monoidal category C.
Dually, a comonoid in a monoidal category C is a monoid in the dual category Cop.
Suppose that the monoidal category C has a symmetry γ. A monoid M in C is commutative when μ ∘ γ = μ.