| Motilin/ghrelin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Structure of motilin in isotropic phospholipid bicellar solution.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Motilin_ghrelin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF04644 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR006738 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1lbj / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 145 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1lbj | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Motilin | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
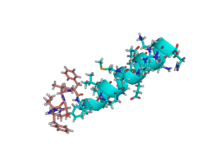 NMR solution structure of motilin in phospholipid bicellar solution.[1] | |||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Symbol | MLN | ||||||
| NCBI gene | 4295 | ||||||
| HGNC | 7141 | ||||||
| OMIM | 158270 | ||||||
| PDB | 1lbj | ||||||
| RefSeq | NM_001040109 | ||||||
| UniProt | P12872 | ||||||
| Other data | |||||||
| Locus | Chr. 6 p21.3-p21.2 | ||||||
| |||||||
Motilin is a 22-amino acid polypeptide hormone in the motilin family that, in humans, is encoded by the MLN gene.[2]
Motilin is secreted by endocrine Mo cells[3][4] (also referred to as M cells, which are not the same as the M cells, or microfold cells, found in Peyer's patches) that are numerous in crypts of the small intestine, especially in the duodenum and jejunum.[5] It is released into the general circulation in humans at about 100-min intervals during the inter-digestive state and is the most important factor in controlling the inter-digestive migrating contractions; and it also stimulates endogenous release of the endocrine pancreas.[6] Based on amino acid sequence, motilin is unrelated to other hormones. Because of its ability to stimulate gastric activity, it was named "motilin." Apart from in humans, the motilin receptor has been identified in the gastrointestinal tracts of pigs, rats, cows, and cats, and in the central nervous system of rabbits.
- ^ a b PDB: 1lbj; Andersson A, Mäler L (October 2002). "NMR solution structure and dynamics of motilin in isotropic phospholipid bicellar solution". Journal of Biomolecular NMR. 24 (2): 103–12. doi:10.1023/A:1020902915969. PMID 12495026. S2CID 34766985.
- ^ Daikh DI, Douglass JO, Adelman JP (October 1989). "Structure and expression of the human motilin gene". DNA. 8 (8): 615–21. doi:10.1089/dna.1989.8.615. PMID 2574660.
- ^ Daniel EE (1990-12-11). Neuropeptide Function in the Gastrointestinal Tract. CRC Press. ISBN 9780849361586.
- ^ Goswami C, Shimada Y, Yoshimura M, Mondal A, Oda S, Tanaka T, Sakai T, Sakata I (2015-06-26). "Motilin Stimulates Gastric Acid Secretion in Coordination with Ghrelin in Suncus murinus". PLOS ONE. 10 (6): e0131554. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1031554G. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0131554. PMC 4482737. PMID 26115342.
- ^ Poitras P, Peeters TL (February 2008). "Motilin". Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity. 15 (1): 54–7. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3282f370af. PMID 18185063. S2CID 220582156.
- ^ Itoh Z (1997). "Motilin and clinical application". Peptides. 18 (4): 593–608. doi:10.1016/S0196-9781(96)00333-6. PMID 9210180. S2CID 38242445.