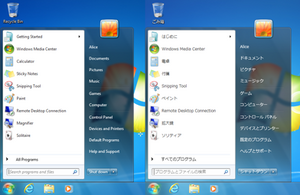
Multilingual User Interface (MUI) enables the localization of the user interface of an application.
MUI is provided by Microsoft as an integrated feature of its operating system Windows 11 down to Windows 2000 with some limitations in older versions.
MUI is used for localizing flagship Microsoft products Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Office and as an open technology can be used in any application that runs in a version of Windows that supports MUI.
The core feature of MUI is the user-defined, system settings for preferred language that can be used/shared by all applications on a computer. The next most core feature is system functions (i.e. LoadString) that use this preference to load user interface assets at runtime from resources in the user's preferred language. To be MUI-enabled, an application need only store user interface assets as language-specific resources and use LoadStrIng to load them at runtime.
MUI also supports storing user interface assets as separate, single-language files which provides for development and deployment flexibility. This feature is optional. The resources can be stored in the application binary.
MUI also provides system functions that allow for custom and extended localization behavior.