| Mycobacteroides abscessus | |
|---|---|
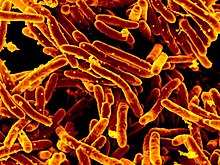
| |
| GD01 strain of Mycobacteroides abscessus isolated from patient | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Actinomycetota |
| Class: | Actinomycetia |
| Order: | Mycobacteriales |
| Family: | Mycobacteriaceae |
| Genus: | Mycobacteroides |
| Species: | M. abscessus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Mycobacteroides abscessus (Moore and Frerichs 1953) Gupta et al. 2018[1]
| |
| Type strain[2] | |
| ATCC 19977 CCUG 20993 CIP 104536 DSM 43491 DSM 44196 Hauduroy L948 JCM 13569 L948 NCTC 13031 TMC 1543 | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Mycobacteroides abscessus (formerly Mycobacterium abscessus[1]) is a species of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) that is a common soil and water contaminant. Although M. abscessus most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), it can also cause infection in almost all human organs, mostly in patients with suppressed immune systems.[3] Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance.[4]

- ^ a b c Gupta, Radhey S.; Lo, Brian; Son, Jeen (2018-02-13). "Phylogenomics and Comparative Genomic Studies Robustly Support Division of the Genus Mycobacterium into an Emended Genus Mycobacterium and Four Novel Genera". Frontiers in Microbiology. 9: 67. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.00067. ISSN 1664-302X. PMC 5819568. PMID 29497402.
- ^ Euzéby JP, Parte AC. "Mycobacteroides abscessus". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved June 24, 2022.
- ^ Song, Joon Young; Sohn, Jang Wook; Jeong, Hye Won; Cheong, Hee Jin; Kim, Woo Joo; Kim, Min Ja (2006-01-13). "An outbreak of post-acupuncture cutaneous infection due to Mycobacterium abscessus". BMC Infectious Diseases. 6: 6. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-6-6. ISSN 1471-2334. PMC 1361796. PMID 16412228.
- ^ Lee; et al. (2015). "Mycobacterium abscesses complex infections in humans". Emerg Infect Dis. 21 (9): 1638–1646. doi:10.3201/2109.141634. PMC 4550155. PMID 26295364.