| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
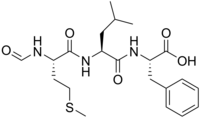
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-2-{(2S)-2-[(2S)-2-Formamido-4-(methylsulfanyl)butanamido]-4-methylpentanamido}-3-phenylpropanoic acid | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | N-Formylmethionine+Leucyl-Phenylalanine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H31N3O5S | |
| Molar mass | 437.56 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Formylmethionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLF, fMLP or N-formyl-met-leu-phe) is an N-formylated tripeptide and sometimes simply referred to as chemotactic peptide is a potent polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) chemotactic factor and is also a macrophage activator.[2]
fMLF is the prototypical representative of the N-formylated oligopeptide family of chemotactic factors. These oligopeptides are known to be, or mimic the actions of, the N-formyl oligopeptides that are (a) released by tissue bacteria, (b) attract and activate circulating blood leukocytes by binding to specific G protein coupled receptors on these cells, and (c) thereby direct the inflammatory response to sites of bacterial invasion. fMLF is involved in the innate immunity mechanism for host defense against pathogens.
fMLF led to the first discovery of a leukocyte receptor for a chemotactic factor, defined three different types of fMLF receptors that have complementary and/or opposing effects on inflammatory responses as well as many other activities, and helped define the stimulus-response coupling mechanisms by which diverse chemotactic factors and their G protein coupled receptors induce cellular function.
- ^ n-formylmethionine leucyl-phenylalanine, Cancerweb
- ^ Panaro MA, Mitolo V (Aug 1999). "Cellular responses to fMLF challenging: a mini-review". Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology. 21 (3): 397–419. doi:10.3109/08923979909007117. PMID 10466071.