| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
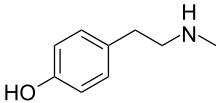
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[2-(Methylamino)ethyl]phenol | |
| Other names
Methyl-4-tyramine; 4-Hydroxy-N-methylphenethylamine; p-(2-Methylaminoethyl)phenol
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.120 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H13NO | |
| Molar mass | 151.209 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.03 g/mL |
| Melting point | 130 to 131 °C (266 to 268 °F; 403 to 404 K) |
| Boiling point | 271 °C (520 °F; 544 K) (183-185 °C at 9mm; 135 °C at 0.05 mm) |
| moderately soluble in water | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Methyltyramine (NMT), also known as 4-hydroxy-N-methylphenethylamine, is a human trace amine[1][2] and natural phenethylamine alkaloid found in a variety of plants.[3] As the name implies, it is the N-methyl analog of tyramine, which is a well-known biogenic trace amine with which NMT shares many pharmacological properties. Biosynthetically, NMT is produced by the N-methylation of tyramine via the action of the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in humans[1][2] and tyramine N-methyltransferase in plants.[4]
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Trace amine template 1was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Trace amine template 2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ T. A. Smith (1977). "Phenethylamine and related compounds in plants." Phytochemistry 16 9 – 18.
- ^ Tyrosine metabolism - Reference pathway Archived 2019-07-26 at the Wayback Machine, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)