| Narva | |
|---|---|
 The Narva flowing between Hermann Castle and Ivangorod Fortress | |
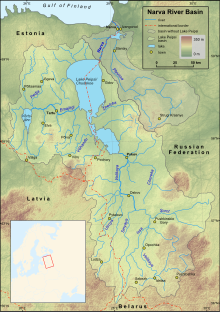 Map of the Narva and Lake Peipus basins | |
| Native name | |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Cities | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Lake Peipus |
| • coordinates | 58°59′14″N 27°43′50″E / 58.98722°N 27.73056°E |
| • elevation | 30 m (98 ft) |
| Mouth | Narva Bay in Finnish Gulf |
• coordinates | 59°28′14″N 28°02′37″E / 59.47056°N 28.04361°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 77 km (48 mi) |
| Basin size | 56,225 km2 (21,709 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 400 m3/s (14,000 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Jaama, Poruni, Mustajõgi |
| • right | Plyussa, Rosson |
| Basin countries | Russia (62.9%), Estonia (30.5%), Latvia (6.6%),[1] Belarus (minute share)(see map) |
The Narva[a], formerly also Narwa or Narova, flows 77 kilometres (48 mi) north into the Baltic Sea and is the largest Estonian river by discharge. A similar length of land far to the south, together with it and a much longer intermediate lake, Lake Peipus, all together nowadays form the international border between Estonia and Russia.
The river gives its name to the archaeological (Neolithic) Narva culture, as well as the city of Narva. Narva is the third most populous urban area in Estonia, and nowadays faces the Russian town of Ivangorod right across the border over the river.
At the coast the river passes part of the resort of Narva-Jõesuu. Its mouth opens into WNW-facing Narva Bay of the Gulf of Finland. Narva gives the second-greatest discharge into the Gulf of Finland (the greatest discharge comes from the Neva River).
- ^ Nõges, Peeter; Järvet, Arvo (2005). "Climate driven changes in the spawning of roach and bream in the Estonian part of the Narva River basin" (PDF). Boreal Environment Research. 10.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).