 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Viracept |
| Other names | NFV |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a697034 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Uncertain; increases when taking with food[1] |
| Protein binding | >98% |
| Metabolism | Liver by CYP including CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 |
| Elimination half-life | 3.5–5 hours |
| Excretion | feces (87%), urine (1–2%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
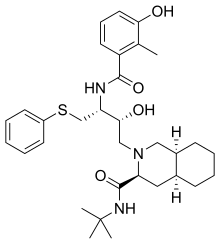
| Formula | C32H45N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 567.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 349.94 °C (661.89 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Nelfinavir, sold under the brand name Viracept, is an antiretroviral medication used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. Nelfinavir belongs to the class of drugs known as protease inhibitors (PIs) and like other PIs is almost always used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs.
Nelfinavir is an orally bioavailable human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1 protease inhibitor (Ki = 2 nM) and is widely prescribed in combination with HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors for the treatment of HIV infection.[2]
It was patented in 1992 and approved for medical use in 1997.[3]
- ^ "Viracept (nelfinavir mesylate) Tablets and Oral Powder, for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). ViiV Healthcare Company. Research Triangle Park, NC 27709. Retrieved 23 November 2015.
- ^ Zhang KE, Wu E, Patick AK, Kerr B, Zorbas M, Lankford A, et al. (April 2001). "Circulating metabolites of the human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitor nelfinavir in humans: structural identification, levels in plasma, and antiviral activities". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 45 (4): 1086–1093. doi:10.1128/AAC.45.4.1086-1093.2001. PMC 90428. PMID 11257019.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 510. ISBN 9783527607495.