| |||
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethylpropane[2] | |||
| Other names
Neopentane
Tetramethylmethane[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1730722 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.677 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1850 | |||
| MeSH | neopentane | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2044 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H12 | |||
| Molar mass | 72.151 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Odor | Odorless | ||
| Density | 3.255 kg/m3 (gas, 9.5 °C) 601.172 kg/m3 (liquid, 9.5 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −16.5 °C (2.3 °F; 256.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 9.5 °C (49.1 °F; 282.6 K) | ||
| Vapor pressure | 146 kPa (at 20 °C)[3] | ||
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
4.7 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
121.07–120.57 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
217 J K−1 mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−168.5–−167.3 kJ mol−1 | ||
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−3.51506–−3.51314 MJ mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H220, H411 | |||
| P210, P273, P377, P381, P391, P403, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related alkanes
|
|||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
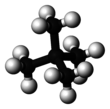
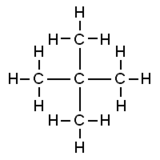
Neopentane, also called 2,2-dimethylpropane, is a double-branched-chain alkane with five carbon atoms. Neopentane is a flammable gas at room temperature and pressure which can condense into a highly volatile liquid on a cold day, in an ice bath, or when compressed to a higher pressure.
Neopentane is the simplest alkane with a quaternary carbon, and has achiral tetrahedral symmetry. It is one of the three structural isomers with the molecular formula C5H12 (pentanes), the other two being n-pentane and isopentane. Out of these three, it is the only one to be a gas at standard conditions; the others are liquids.
It was first synthesized by Russian chemist Mikhail Lvov in 1870.[4]
- ^ Aston, J.G.; Messerly, G.H., Heat Capacities and Entropies of Organic Compounds II. Thermal and Vapor Pressure Data for Tetramethylmethane from 13.22K to the Boiling Point. The Entropy from its Raman Spectrum, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1936, 58, 2354.
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 652. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ "Neopentane | C5H12 - PubChem".
- ^ Zeitschrift für Chemie (in German). Quandt & Händel. 1870.