| Neural plate | |
|---|---|
 Neural crest | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 9 |
| Days | 19 |
| Precursor | Ectoderm |
| Gives rise to | Neural folds |
| System | Central nervous system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lamina neuralis |
| MeSH | D054258 |
| TE | plate_by_E5.13.1.0.1.0.1 E5.13.1.0.1.0.1 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
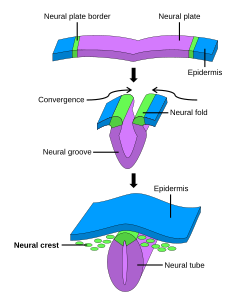
In embryology, the neural plate is a key developmental structure that serves as the basis for the nervous system. Cranial to the primitive node of the embryonic primitive streak, ectodermal tissue thickens and flattens to become the neural plate. The region anterior to the primitive node can be generally referred to as the neural plate. Cells take on a columnar appearance in the process as they continue to lengthen and narrow. The ends of the neural plate, known as the neural folds, push the ends of the plate up and together, folding into the neural tube, a structure critical to brain and spinal cord development. This process as a whole is termed primary neurulation.[1]
Signaling proteins are also important in neural plate development, and aid in differentiating the tissue destined to become the neural plate. Examples of such proteins include bone morphogenetic proteins and cadherins. Expression of these proteins is essential to neural plate folding and subsequent neural tube formation.
- ^ Gilbert, Scott F. (2010). Developmental biology (9th. ed.). Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer Associates. pp. 333–338. ISBN 978-0878933846.