 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Viramune |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a600035 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 93% ± 9% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 45 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney: <6% (Parent drug) Bile duct <5% (Parent drug) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.117.250 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
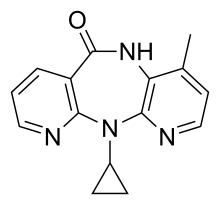
| Formula | C15H14N4O |
| Molar mass | 266.304 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Nevirapine (NVP), sold under the brand name Viramune among others, is a medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS, specifically HIV-1.[5] It is generally recommended for use with other antiretroviral medications.[5] It may be used to prevent mother to child spread during birth but is not recommended following other exposures.[5] It is taken by mouth.[5]
Common side effects include rash, headache, nausea, feeling tired, and liver problems.[5] The liver problems and skin rash may be severe and should be checked for during the first few months of treatment.[5][6] It appears to be safe for use during pregnancy.[5] It is a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) and works by blocking the function of reverse transcriptase.[5]
Nevirapine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[7] It is available as a generic medication.[5]
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ "Prescription medicines: registration of new generic medicines and biosimilar medicines, 2017". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 June 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Viramune FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Viramune XR FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Nevirapine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 3 December 2016.
- ^ Hamilton R (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 63. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.