| Night shark | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Order: | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family: | Carcharhinidae |
| Genus: | Carcharhinus |
| Species: | C. signatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Carcharhinus signatus (Poey, 1868)
| |
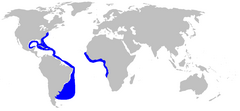
| |
| Range of the night shark | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Hypoprion bigelowi Cadenat, 1956 | |
The night shark (Carcharhinus signatus) is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae, found in the temperate and tropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean. An inhabitant of the outer continental shelf and upper continental slope, this shark most commonly occurs at depths of 50–600 m (160–1,970 ft) and conducts a diel vertical migration, spending the day in deeper water and moving into shallower waters at night. Off northeastern Brazil, large numbers congregate around seamounts of varying depths. A slender, streamlined species, the night shark typically reaches a length of 2 m (6.6 ft). It can be identified by its long, pointed snout and large, green eyes (when alive), and is dark grayish blue or brown above and white below.
Night sharks are quick, nocturnally active, schooling predators that feed mainly on small bony fishes and squid. Reproduction is viviparous as with the other members of its family; females mate during the summer and give birth to litters of usually 12–18 pups after a gestation period of a year. This deepwater species is not known to pose a danger to humans. It is caught incidentally by commercial tuna and swordfish longline fisheries in the western Atlantic, and also by a targeted longline fishery operating off northeastern Brazil. The night shark is highly valued for its fins, and additionally as a source of meat, liver oil, and fishmeal. However, most sharks caught off northeastern Brazil have been found to contain unsafe concentrations of mercury.
Because of its low reproductive rate and historically documented declines in areas such as the Caribbean, the night shark has been assessed as vulnerable by the American Fisheries Society. A population assessment has indicated that this species is secure in the waters off the United States, but this may not be true elsewhere.
- ^ Carlson, J., Charvet, P., Blanco-Parra, MP, Briones Bell-lloch, A., Cardenosa, D., Crysler, Z., Espinoza, E., Herman, K., Morales-Saldaña, J.M., Naranjo-Elizondo, B., Pacoureau, N., Pérez Jiménez, J.C., Schneider, E.V.C., Simpson, N.J. & Talwar, B.S. (2021). "Carcharhinus signatus". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021. IUCN: e.T60219A3094326. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T60219A3094326.en. S2CID 241029249.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
