 | |
 | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Nirmatrelvir | Antiviral drug |
| Ritonavir | CYP3A inhibitor; Antiviral drug |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Paxlovid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a622005 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
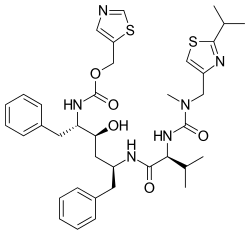
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, sold under the brand name Paxlovid, is a co-packaged medication used as a treatment for COVID‑19.[8][11][10][18] It contains the antiviral medications nirmatrelvir and ritonavir and was developed by Pfizer.[8][10] Nirmatrelvir inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease, while ritonavir is a strong CYP3A inhibitor, slowing down nirmatrelvir metabolism and therefore boosting its effect.[10][19] It is taken by mouth.[10]
In unvaccinated high-risk people with COVID‑19, nirmatrelvir/ritonavir can reduce the risk of hospitalization or death by 88% if taken within five days of symptom onset.[20] People who take nirmatrelvir/ritonavir also test negative for COVID‑19 about two and a half days earlier than people who do not.[21] Side effects of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir include changes in sense of taste (dysgeusia), diarrhea, high blood pressure (hypertension), and muscle pain (myalgia).[10]
In December 2021, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted nirmatrelvir/ritonavir emergency use authorization (EUA) to treat COVID‑19.[13][22] It was approved in the United Kingdom later that month,[23] and in the European Union and Canada in January 2022.[15][24][25] In May 2023, it was approved in the U.S. to treat mild to moderate COVID‑19 in adults who are at high risk for progression to severe COVID‑19, including hospitalization or death.[14][18] The FDA considers the combination to be a first-in-class medication.[26] In 2022, it was the 164th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions.[27][28]
- ^ "Paxlovid APMDS". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 January 2022. Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- ^ a b "TGA eBS - Product and Consumer Medicine Information Licence". Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ "Product Monograph: Paxlovid" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 January 2024.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Paxlovid". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 12 June 2022. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Paxlovid detailswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c "Summary of Product Characteristics for Paxlovid". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ "Regulatory approval of Paxlovid". Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f "Paxlovid- nirmatrelvir and ritonavir kit". DailyMed. 18 October 2023. Archived from the original on 26 February 2024. Retrieved 6 January 2024.
- ^ a b "Paxlovid- nirmatrelvir and ritonavir kit". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
FDA PR 20211222was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Fact sheet for healthcare providers: Emergency Use Authorization for Paxlovid (PDF) (Technical report). Pfizer. 22 December 2021. LAB-1492-0.8. Archived from the original on 23 December 2021.
- ^ a b "FDA Approves First Oral Antiviral for Treatment of COVID-19 in Adults". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 26 May 2023. Archived from the original on 28 July 2023. Retrieved 26 May 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b "Paxlovid EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 24 January 2022. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ "Paxlovid PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 28 January 2022. Archived from the original on 16 May 2022. Retrieved 24 April 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19 medicines". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 14 October 2024. Retrieved 14 October 2024.
- ^ a b "Frequently Asked Questions on the Emergency Use Authorization for Paxlovid for Treatment of COVID-19" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 1 November 2023. Archived from the original on 7 January 2024. Retrieved 6 January 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pmid36423149was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
NEJM Hammondwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Amani B, Amani B (February 2023). "Efficacy and safety of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for COVID-19: A rapid review and meta-analysis". Journal of Medical Virology. 95 (2): e28441. doi:10.1002/jmv.28441. PMC 9880713. PMID 36576379.
- ^ "Pfizer Receives U.S. FDA Emergency Use Authorization for Novel COVID-19 Oral Antiviral Treatment" (Press release). Pfizer. 22 December 2021. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 22 December 2021 – via Business Wire.
- ^ "Oral COVID-19 antiviral, Paxlovid, approved by UK regulator" (Press release). Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 11 January 2022. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ "Health Canada authorizes Paxlovid for patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 at high risk of developing serious disease". Health Canada (Press release). 17 January 2022. Archived from the original on 29 April 2022. Retrieved 24 April 2022.
- ^ "Paxlovid". COVID-19 vaccines and treatments portal. 17 January 2022. Archived from the original on 22 April 2022. Retrieved 25 April 2022.
- ^ New Drug Therapy Approvals 2023 (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Report). January 2024. Archived from the original on 10 January 2024. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Nirmatrelvir; Ritonavir Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.