 |
| Information mapping |
|---|
| Topics and fields |
| Node–link approaches |
|
| See also |
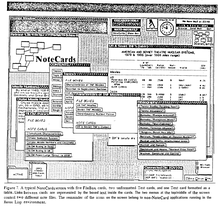
NoteCards was a hypertext-based personal knowledge base system developed at Xerox PARC by Randall Trigg, Frank Halasz and Thomas Moran in 1984.[1][2] NoteCards was developed after Trigg's pioneering 1983 Ph.D. thesis on hypertext while at the University of Maryland College Park.
NoteCards was built to model four basic kinds of objects: notecards, links, browser card, and a filebox.[3] Each window is an analog of a cue card; window sizes may vary, but contents cannot scroll. Local and global maps are available through browsers. There are over 40 different nodes which support various media.
The basic construct in NoteCards is a semantic network composed of notecards connected by typed links. Each notecard contains an arbitrary amount of information embodied in text, graphics, images, or some other editable substance. Links are used to represent binary connections between cards. NoteCards provides two specialized types of cards, Browsers and FileBoxes, that help the user to manage networks of cards and links.
— "Notecards in a nutshell" (1987)[1]
NoteCards was implemented in LISP on D-machine workstations from Xerox which used large, high-resolution displays. The NoteCards interface is event-driven. One interesting feature of NoteCards is that authors may use LISP commands to customize or create entirely new node types. The powerful programming language allows almost complete customization of the entire NoteCards work environment.
- ^ a b Halasz, Frank G.; Thomas P. Moran; Randall H. Trigg (1987). "Notecards in a nutshell". Proceedings of the SIGCHI/GI conference on Human factors in computing systems and graphics interface. Toronto, Ontario, Canada: ACM Press. pp. 45–52. doi:10.1145/29933.30859. ISBN 0-89791-213-6.
- ^ Conklin, Jeff (September 1987). "Hypertext: an introduction and survey" (PDF). IEEE Computer. 20 (9): 17–41. doi:10.1109/MC.1987.1663693. S2CID 9188803.
- ^ Halasz, Frank G. (2001). "Reflections on NoteCards: seven issues for the next generation of hypermedia systems". ACM Journal of Computer Documentation. 25 (3): 71–87. doi:10.1145/507317.507321. S2CID 53245008.