| Oirat | |
|---|---|
| Oirat Mongolian | |
| ᡆᡕᡅᠷᠠᡑ ᡘᡄᠯᡄᠨ Oirad kelen Өөрд келн ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠬᠡᠯᠡᠨ ᠦ ᠣᠶᠢᠷᠠᠳ ᠠᠶᠠᠯᠭᠤ Mongγol kelen-ü Oyirad ayalγu Моңһл келнә Өөрд айлһ | |
| Pronunciation | [øːˈrət keˈlən] |
| Native to | Mongolia, Russia, China, Kyrgyzstan[1] |
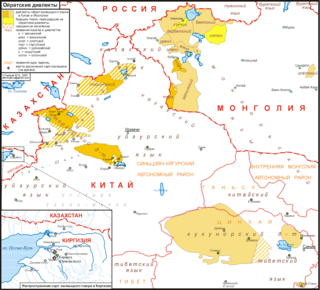
| Region | Khovd, Uvs,[2] Bayan-Ölgii,[3] Kalmykia, Xinjiang, Gansu, Qinghai |
| Ethnicity | 655,372 Oirats |
Native speakers | 368,000, 58% of ethnic population (2007–2010)[4] |
Standard forms | |
| Clear script (China: unofficial), Cyrillic (Russia: official) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Kalmykia, Russia (in the form of Kalmyk); Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Qinghai, China; Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture and Bortala Mongol Autonomous Prefecture in Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | xal Kalmyk |
| ISO 639-3 | Either:xal – Kalmyk Oiratxwo – Written Oirat |
xwo Written Oirat | |
| Glottolog | kalm1243 |
| Linguasphere | of 44-BAA-b part of 44-BAA-b |
 | |
Oirat (Clear script: ᡆᡕᡅᠷᠠᡑ
ᡍᡄᠯᡄᠨ, Oirad kelen; Kalmyk: Өөрд, Öörd [øːˈrət]; Khalkha Mongolian: Ойрад, Oirad [ˈœe̯rət]) is a Mongolic language spoken by the descendants of Oirat Mongols, now forming parts of Mongols in China, Kalmyks in Russia and Mongolians. Largely mutually intelligible to other core Central Mongolic languages, scholars differ as to whether they regard Oirat as a distinct language[6] or a major dialect of the Mongolian language.[7] Oirat-speaking areas are scattered across the far west of Mongolia,[8] the northwest of China[8] and Russia's Caspian coast, where its major variety is Kalmyk.[9] In China, it is spoken mainly in Xinjiang, but also among the Deed Mongol of Qinghai and Subei County in Gansu.[8]
In all three countries, Oirat has become variously endangered or even obsolescent as a direct result of government actions or as a consequence of social and economic policies. Its most widespread tribal dialect, which is spoken in all of these nations, is Torgut.[1][8] The term Oirat or more precisely, Written Oirat is sometimes also used to refer to the language of historical documents written in the Clear script.[10]
- ^ a b Svantesson et al. 2005: 148
- ^ Svantesson et al. 2005: 141
- ^ Coloo 1988: 1
- ^ Kalmyk Oirat at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
Written Oirat at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required) - ^ cp. the distribution given by Svantesson et al. 2005: 141
- ^ Birtalan 2003. Note that she is not altogether clear about that matter as she writes: "For the present purpose, Spoken Oirat, from which Kalmuck is excluded, may therefore be treated as a more or less uniform language." (212). See also Sanžeev 1953
- ^ Sečenbaγatur et al. 2005
- ^ a b c d Sečenbaγatur et al. 2005: 396-398
- ^ Sečenbaγatur et al. 2005, Bläsing 2003: 229
- ^ Birtalan 2003: 210-211