| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
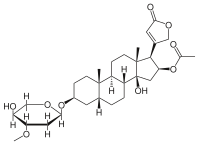
| IUPAC name
16β-(Acetyloxy)-3β-(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-α-L-arabino-hexopyranosyloxy)-14-hydroxy-5β-card-20(22)-enolide
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,2S,3aS,3bR,5aR,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-3a-Hydroxy-7-{[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-9a,11a-dimethyl-1-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-yl)hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-2-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.693 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H48O9 | |
| Molar mass | 576.72 g/mol |
| Appearance | Oleandrin forms colourless, odourless, acicular crystals that are very bitter |
| Density | 1.261 g/ml |
| Melting point | 250.0 °C (482.0 °F; 523.1 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Acute Toxicity (Oral, inhalation) |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H330, H373 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P284, P301+P310, P304+P340, P310, P320, P330, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
0.248 mg/kg (Cat, Intravenous) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Safety Data Sheet |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Oleandrin is a cardiac glycoside found in the poisonous plant oleander (Nerium oleander L.).[1] As a main phytochemical of oleander, oleandrin is associated with the toxicity of oleander sap, and has similar properties to digoxin.[1]
Oleander has been used in traditional medicine for its presumed therapeutic purposes, such as for treating cardiac insufficiency. There is no clinical evidence that oleander or its constituents, including oleandrin, are safe or effective. Oleandrin is not approved by regulatory agencies as a prescription drug or dietary supplement.[1]
- ^ a b c "Oleander". Drugs.com. 1 December 2018. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
