| Optic disc drusen | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Optic nerve head drusen |
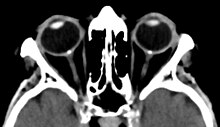 | |
| Bilateral optic disc drusen in computed tomography seen as dense spots at the optical disc | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Optic disc drusen (ODD) are globules of mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides that progressively calcify in the optic disc.[1][2] They are thought to be the remnants of the axonal transport system of degenerated retinal ganglion cells.[3][4][5] ODD have also been referred to as congenitally elevated or anomalous discs, pseudopapilledema, pseudoneuritis, buried disc drusen, and disc hyaline bodies.[6]
- ^ Golnik, K. (2006). Congenital anomalies and acquired abnormalities of the optic nerve, (Version 14.3). UptoDate (On-Line Serial)
- ^ Friedman AH, Henkind P, Gartner S (April 1975). "Drusen of the optic disc. A histopathological study". Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 95 (1): 4–9. PMID 1064209.
- ^ Rosen E, Almog Y, Assia E (November 2005). "[Optic disc drusen and acute vision loss]". Harefuah (in Hebrew). 144 (11): 785–89, 822. PMID 16358654.
- ^ Tso MO (October 1981). "Pathology and pathogenesis of drusen of the optic nervehead". Ophthalmology. 88 (10): 1066–80. doi:10.1016/s0161-6420(81)80038-3. PMID 7335311.
- ^ Kapur R, Pulido JS, Abraham JL, Sharma M, Buerk B, Edward DP (January 2008). "Histologic findings after surgical excision of optic nerve head drusen". Retina. 28 (1): 143–46. doi:10.1097/IAE.0b013e31815e98d8. PMID 18185151. S2CID 21285492.
- ^ "Optic Nerve Head Drusen". Handbook of Ocular Disease Management. Jobson Publishing L.L.C. 2001. Archived from the original on 2004-12-09.