| Otitis media | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Otitis media with effusion: serous otitis media, secretory otitis media |
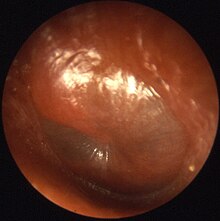 | |
| A bulging tympanic membrane which is typical in a case of acute otitis media | |
| Specialty | Otorhinolaryngology |
| Symptoms | Ear pain, fever, hearing loss[1][2] |
| Types | Acute otitis media, otitis media with effusion, chronic suppurative otitis media[3][4] |
| Causes | Viral, bacterial[4] |
| Risk factors | Smoke exposure, daycare[4] |
| Prevention | Vaccination, breastfeeding[1] |
| Medication | Paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops[1] |
| Frequency | 471 million (2015)[5] |
| Deaths | 3,200 (2015)[6] |
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear.[2] One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM),[3] an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain.[1] In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep.[1] Decreased eating and a fever may also be present.[1] The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms,[1] although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described;[4] it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media.[4] Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks.[7] It may be a complication of acute otitis media.[4] Pain is rarely present.[4] All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss.[2][3] If children with hearing loss due to OME do not learn sign language, it may affect their ability to learn.[8]
The cause of AOM is related to childhood anatomy and immune function.[4] Either bacteria or viruses may be involved.[4] Risk factors include exposure to smoke, use of pacifiers, and attending daycare.[4] It occurs more commonly among indigenous Australians and those who have cleft lip and palate or Down syndrome.[4][9] OME frequently occurs following AOM and may be related to viral upper respiratory infections, irritants such as smoke, or allergies.[3][4] Looking at the eardrum is important for making the correct diagnosis.[10] Signs of AOM include bulging or a lack of movement of the tympanic membrane from a puff of air.[1][11] New discharge not related to otitis externa also indicates the diagnosis.[1]
A number of measures decrease the risk of otitis media including pneumococcal and influenza vaccination, breastfeeding, and avoiding tobacco smoke.[1] The use of pain medications for AOM is important.[1] This may include paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, benzocaine ear drops, or opioids.[1] In AOM, antibiotics may speed recovery but may result in side effects.[12] Antibiotics are often recommended in those with severe disease or under two years old.[11] In those with less severe disease they may only be recommended in those who do not improve after two or three days.[11] The initial antibiotic of choice is typically amoxicillin.[1] In those with frequent infections tympanostomy tubes may decrease recurrence.[1] In children with otitis media with effusion antibiotics may increase resolution of symptoms, but may cause diarrhoea, vomiting and skin rash.[13]
Worldwide AOM affects about 11% of people a year (about 325 to 710 million cases).[14][15] Half the cases involve children less than five years of age and it is more common among males.[4][14] Of those affected about 4.8% or 31 million develop chronic suppurative otitis media.[14] The total number of people with CSOM is estimated at 65–330 million people.[16] Before the age of ten OME affects about 80% of children at some point.[4] Otitis media resulted in 3,200 deaths in 2015 – down from 4,900 deaths in 1990.[6][17]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Lieberthal AS, Carroll AE, Chonmaitree T, Ganiats TG, Hoberman A, Jackson MA, et al. (March 2013). "The diagnosis and management of acute otitis media". Pediatrics. 131 (3): e964–999. doi:10.1542/peds.2012-3488. PMID 23439909.
- ^ a b c Qureishi A, Lee Y, Belfield K, Birchall JP, Daniel M (January 2014). "Update on otitis media – prevention and treatment". Infection and Drug Resistance. 7: 15–24. doi:10.2147/IDR.S39637. PMC 3894142. PMID 24453496.
- ^ a b c d "Ear Infections". cdc.gov. September 30, 2013. Archived from the original on 19 February 2015. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Minovi A, Dazert S (2014). "Diseases of the middle ear in childhood". GMS Current Topics in Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery. 13: Doc11. doi:10.3205/cto000114. PMC 4273172. PMID 25587371.
- ^ Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Brown A, et al. (GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- ^ a b Wang H, Naghavi M, Allen C, Barber RM, Bhutta ZA, Carter A, et al. (GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators) (October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- ^ Emmett SD, Kokesh J, Kaylie D (November 2018). "Chronic Ear Disease". The Medical Clinics of North America. 102 (6): 1063–1079. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2018.06.008. PMID 30342609. S2CID 53045631.
- ^ Ruben RJ, Schwartz R (February 1999). "Necessity versus sufficiency: the role of input in language acquisition". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 47 (2): 137–140. doi:10.1016/S0165-5876(98)00132-3. PMID 10206361. Archived from the original on 2018-06-14. Retrieved 2021-09-27.
- ^ "Ear disease in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children" (PDF). AIHW. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 February 2017. Retrieved 12 May 2017.
- ^ Coker TR, Chan LS, Newberry SJ, Limbos MA, Suttorp MJ, Shekelle PG, et al. (November 2010). "Diagnosis, microbial epidemiology, and antibiotic treatment of acute otitis media in children: a systematic review". JAMA. 304 (19): 2161–2169. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1651. PMID 21081729.
- ^ a b c "Otitis Media: Physician Information Sheet (Pediatrics)". cdc.gov. November 4, 2013. Archived from the original on 10 September 2015. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ Venekamp RP, Sanders SL, Glasziou PP, Rovers MM (2023-11-15). "Antibiotics for acute otitis media in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 11 (11): CD000219. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000219.pub5. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 10646935. PMID 37965923.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC embargo expired (link) - ^ Venekamp RP, Burton MJ, van Dongen TM, van der Heijden GJ, van Zon A, Schilder AG (June 2016). "Antibiotics for otitis media with effusion in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016 (6): CD009163. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009163.pub3. PMC 7117560. PMID 27290722.
- ^ a b c Monasta L, Ronfani L, Marchetti F, Montico M, Vecchi Brumatti L, Bavcar A, et al. (2012). "Burden of disease caused by otitis media: systematic review and global estimates". PLOS ONE. 7 (4): e36226. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...736226M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036226. PMC 3340347. PMID 22558393.
- ^ Vos T, Barber RM, Bell B, Bertozzi-Villa A, Biryukov S, Bolliger I, et al. (Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators) (August 2015). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 386 (9995): 743–800. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(15)60692-4. PMC 4561509. PMID 26063472.
- ^ Erasmus T (2012-09-17). "Chronic suppurative otitis media". Continuing Medical Education. 30 (9): 335–336–336. ISSN 2078-5143. Archived from the original on 2020-10-20. Retrieved 2019-08-07.
- ^ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators (January 2015). "Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013". Lancet. 385 (9963): 117–171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. PMC 4340604. PMID 25530442.
{{cite journal}}:|author1=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)