| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Oxazole[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 103851 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.474 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 485850 | |||
| MeSH | D010080 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H3NO | |||
| Molar mass | 69.06 g/mol | ||
| Density | 1.050 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 69.5 °C (157.1 °F; 342.6 K) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.8 (of conjugate acid)[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling:[3] | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H318 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264+P265, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P354+P338, P317, P370+P378, P403+P235, P501 | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Oxazole (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
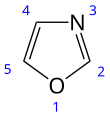
Oxazole is the parent compound for a vast class of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds. These are azoles with an oxygen and a nitrogen separated by one carbon.[4] Oxazoles are aromatic compounds but less so than the thiazoles. Oxazole is a weak base; its conjugate acid has a pKa of 0.8, compared to 7 for imidazole.
- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 140. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ Zoltewicz, J. A. & Deady, L. W. Quaternization of heteroaromatic compounds. Quantitative aspects. Adv. Heterocycl. Chem. 22, 71-121 (1978).
- ^ "Oxazole". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ T. L. Gilchrist (1997). Heterocyclic Chemistry (3 ed.). Longman. ISBN 0-582-01421-2.