| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
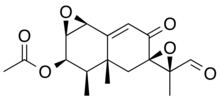
| IUPAC name
(11S)-8,12-Dioxo-1β,2β:7,11-diepoxy-7α-eremophil-9-en-3β-yl acetate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1aR,2R,2′R,3R,3′S,3aR,7bS)-3′-Formyl-3,3′,3a-trimethyl-6-oxo-1a,2,3a,4,6,7b-hexahydro-3H-spiro[naphtho[1,2-b]oxirene-5,2′-oxiran]-2-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Penicillin Roquefort toxin (PR toxin) is a mycotoxin produced by the fungus Penicillium roqueforti. In 1973, PR toxin was first partially characterized by isolating moldy corn on which the fungi had grown.[1] Although its lethal dose was determined shortly after the isolation of the chemical, details of its toxic effects were not fully clarified until 1982 in a study with mice, rats, anesthetized cats and preparations of isolated rat auricles.[2]
- ^ Wei, R.D.; et al. (1973-01-25). "Isolation and Partial Characterization of a Mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti". American Society for Microbiology. 25 (1): 111–114. doi:10.1128/am.25.1.111-114.1973. PMC 380745. PMID 4687064.
- ^ Chen, F.C.; et al. (1982). "Acute toxicity of PR toxin, a mycotoxin from Penicillium roqueforti'". Toxicon. 20 (2): 433–441. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(82)90006-x. PMID 7080052.