| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
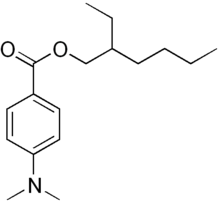
| IUPAC name
2-ethylhexyl 4-(dimethylamino)benzoate
| |
| Other names
2-ethylhexyl dimethyl PABA
Escalol 507 Sundown | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.248 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H27NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 277.408 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.99 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | <25 °C |
| Boiling point | 362 °C (684 °F; 635 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Padimate O is an organic compound related to the water-soluble compound PABA (4-aminobenzoic acid) that is used as an ingredient in some sunscreens. This yellowish water-insoluble oily liquid is an ester formed by the condensation of 2-ethylhexanol with dimethylaminobenzoic acid. Other names for padimate O include 2-ethylhexyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate, Escalol 507, octyldimethyl PABA, and OD-PABA.
