
| |
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H20 | |
| Molar mass | 260.380 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.629 g/ml |
| Structure | |
| D2h | |
| 0 D | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
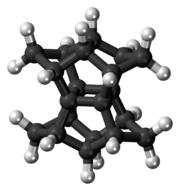
Pagodane is an organic compound with formula C
20H
20 whose carbon skeleton was said to resemble a pagoda, hence the name.[1] It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon whose molecule has the D2h point symmetry group. The compound is a highly crystalline solid that melts at 243 °C, is barely soluble in most organic solvents and moderately soluble in benzene and chloroform. It sublimes at low pressure.[2]
The name pagodane is used more generally for any member of a family of compounds whose molecular skeletons have the same 16-carbon central cage as the basic compound. Each member can be seen as the result of connecting eight atoms of this cage in pairs by four alkane chains. The general member is denoted [m.n.p.q]pagodane where m, n, p and q are the number of carbons of those four chains. The general formula is then C
16+sH
12+2s where s= m+n+p+q. In particular, the basic compound C
20H
20 has those carbons connected by four methylene bridges (m=n=p=q=1), and its name within that family is therefore [1.1.1.1]pagodane.[2]