| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
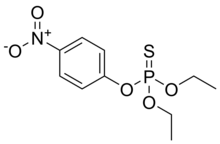
| Preferred IUPAC name
O,O-Diethyl O-(4-nitrophenyl) phosphorothioate | |
| Other names
E605
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 2059093 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.247 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3018 2783 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14NO5PS | |
| Molar mass | 291.26 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals (pure form) |
| Melting point | 6 °C (43 °F; 279 K) |
| 24 mg/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | high solubility |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H311, H330, H372, H410 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P310, P312, P314, P320, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 120 °C (248 °F; 393 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
5 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 10 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 3 mg/kg (dog, oral) 0.93 mg/kg (cat, oral) 5 mg/kg (horse, oral) 8 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2 mg/kg (rat, oral)[3] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
84 mg/m3 (rat, 4 hr)[3] |
LCLo (lowest published)
|
50 mg/m3 (rabbit, 2 hr) 14 mg/m3 (guinea pig, 2 hr) 15 mg/m3 (mouse)[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
none (methyl parathion),[1] TWA 0.1 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.2 mg/m3 [skin] (methyl parathion)[1] TWA 0.05 mg/m3 [skin] (ethyl parathion)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D. (methyl parathion)[1] 10 mg/m3 (ethyl parathion)[2] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | [1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Parathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally[clarification needed] known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.[5]
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0427". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0479". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b c "Parathion". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Hazard Rating Information for NFPA Fire Diamonds". Archived from the original on 2015-02-17. Retrieved 2015-03-13.
- ^ "Parathion". www.fao.org. Retrieved 2020-04-17.
